Custom Online Plastic 3D Printing Service
Our Online Plastic Parts 3D Printing Service offers high-quality manufacturing using advanced technologies like FDM, SLA, SLS, and more. We support various plastic materials, ensuring precision, durability, and customization for prototypes, functional parts, and production-ready components.
- Material Extrusion 3D Printing
- Vat Photopolymerization 3D Printing
- Powder Bed Fusion 3D Printing
- Material Jetting 3D Printing

Send us your designs and specifications for a free quotation
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
Plastic 3D Printing Technologies
Plastic 3D printing technologies, including FDM, SLA, SLS, and PolyJet, offer versatile solutions for prototypes and functional parts. They support thermoplastics, photopolymers, and powders, ensuring precision, durability, and cost-effectiveness for complex designs across various industries and applications.
Plastic 3D Printing Materials
Applications of Plastic 3D Printed Parts
Plastic 3D printed parts are popular due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and the wide range of properties they can exhibit, from high flexibility to significant strength. These parts are extensively used in industries like consumer goods, automotive, and medical devices for their ability to form complex shapes and lightweight structures.
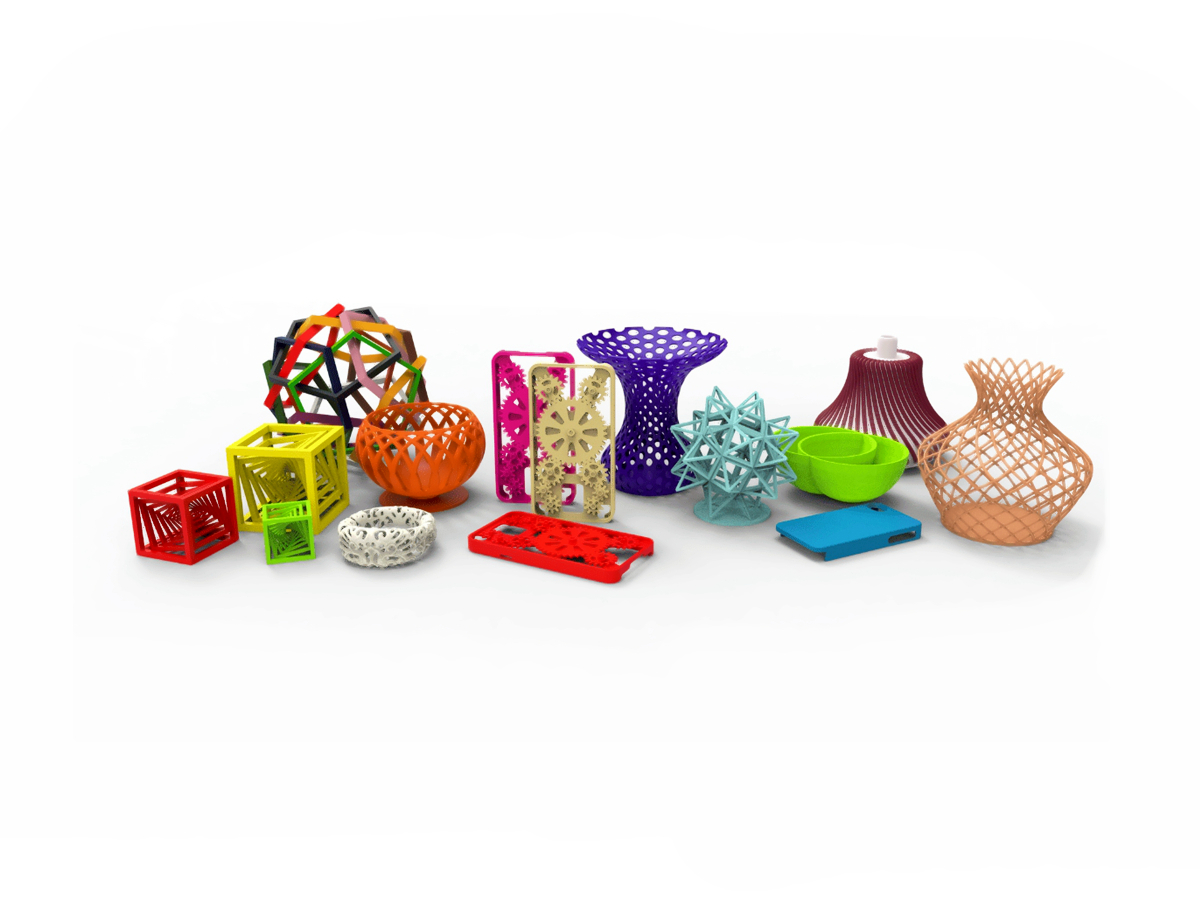
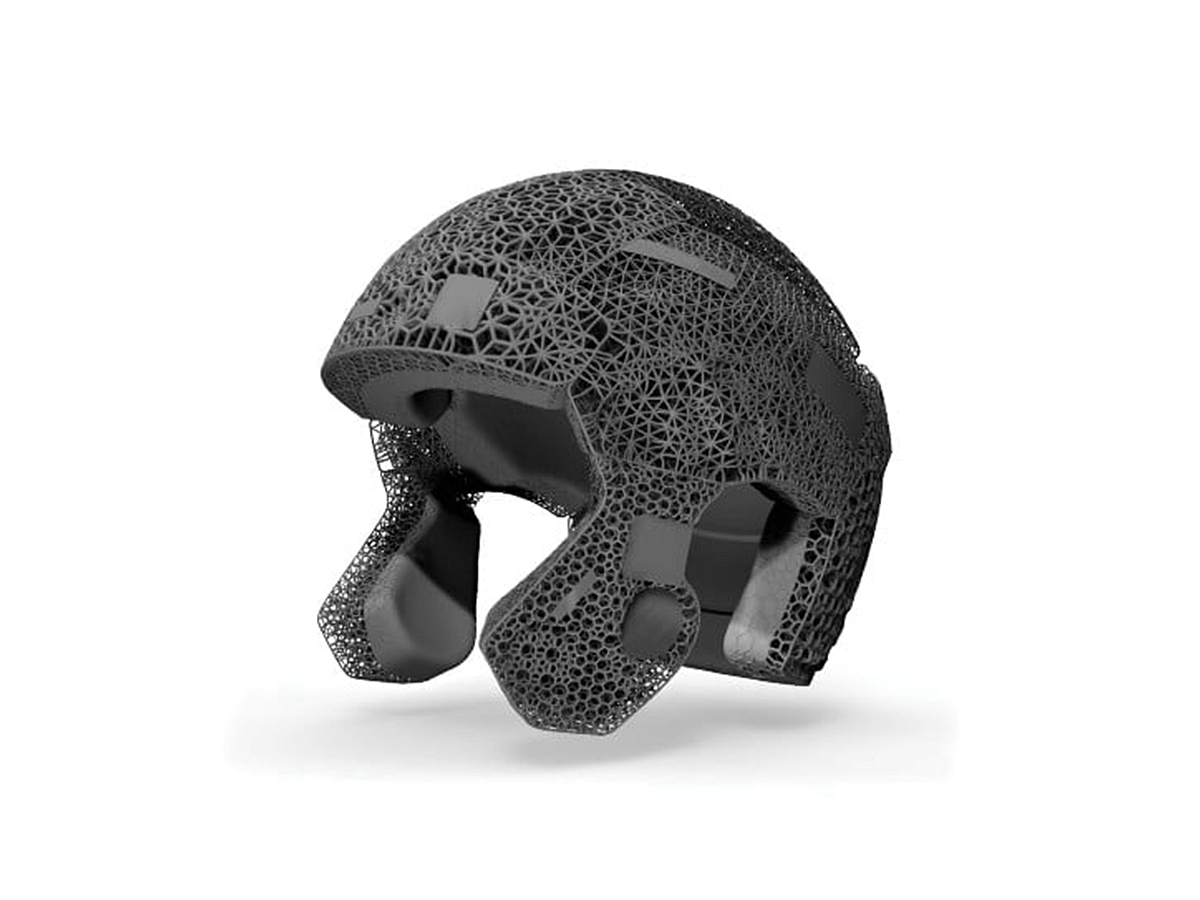
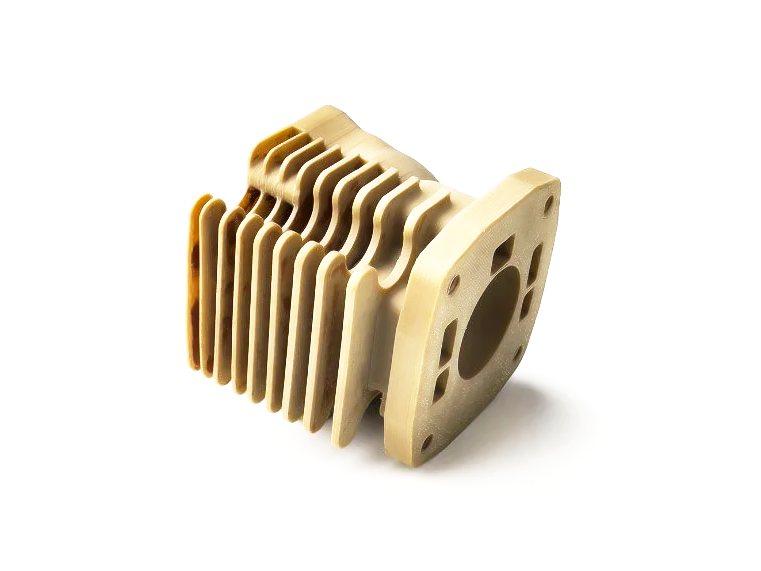
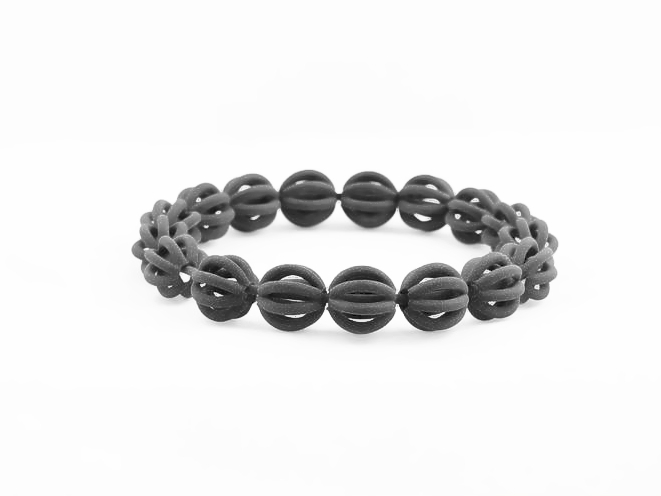
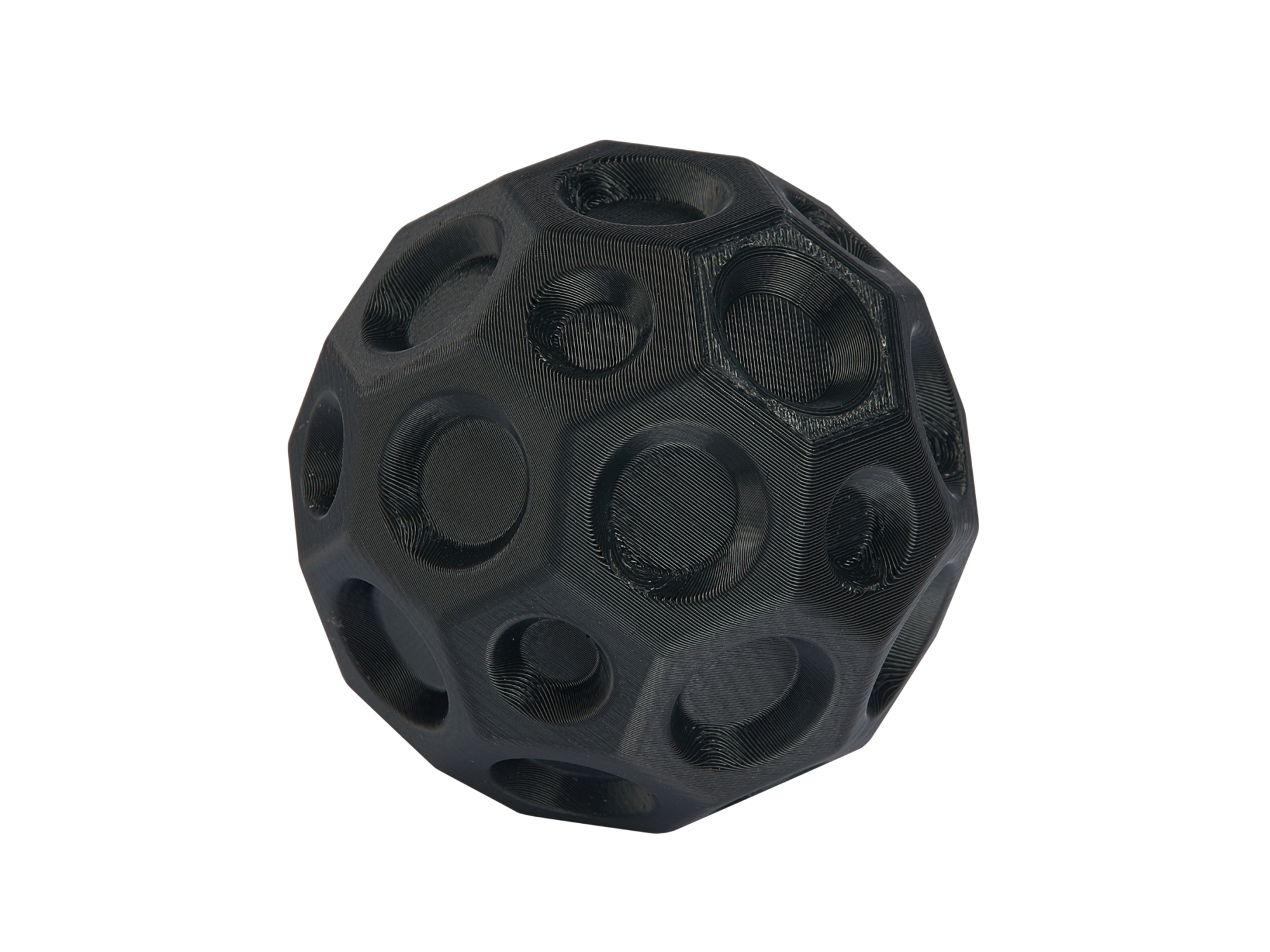
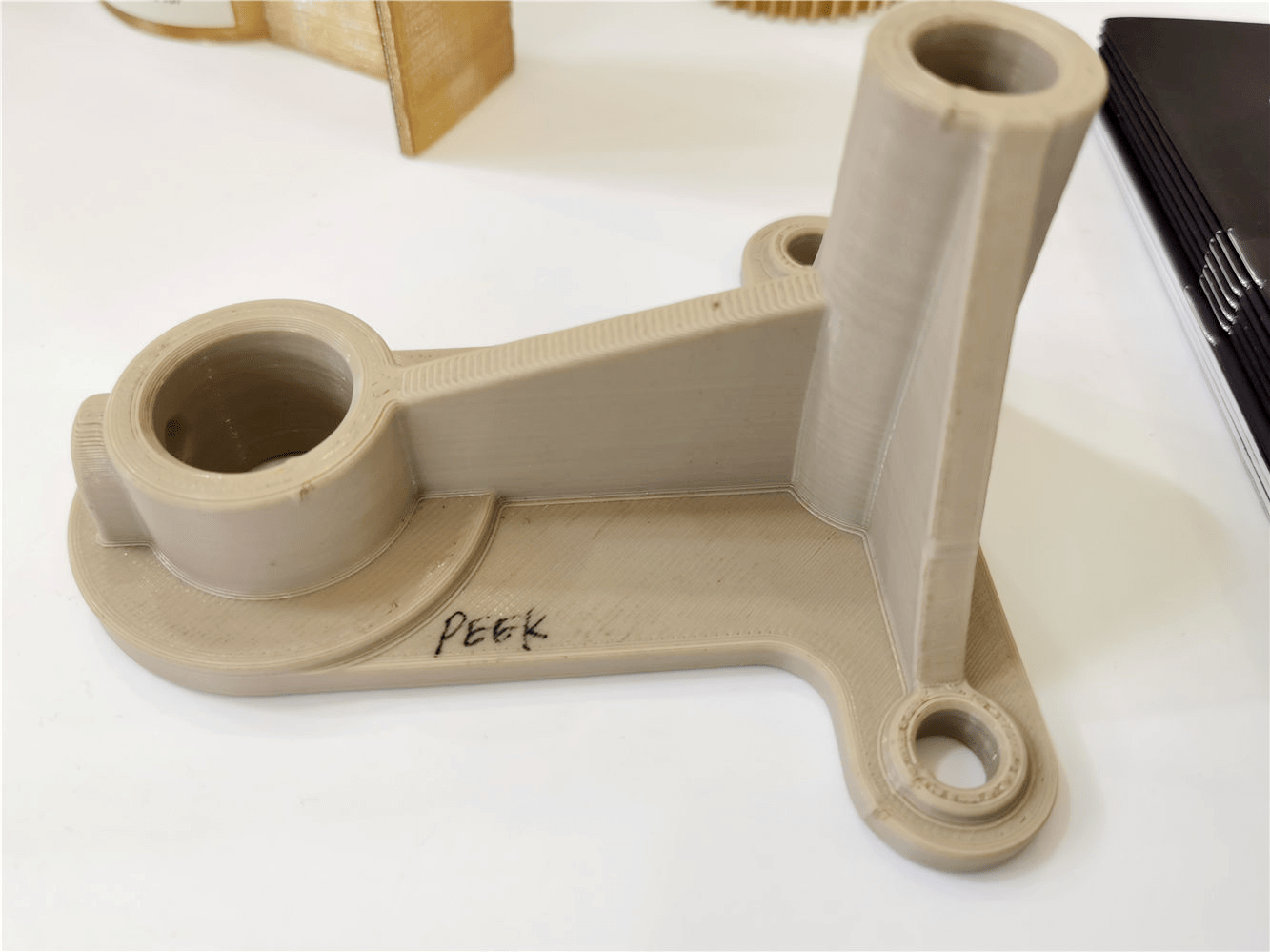
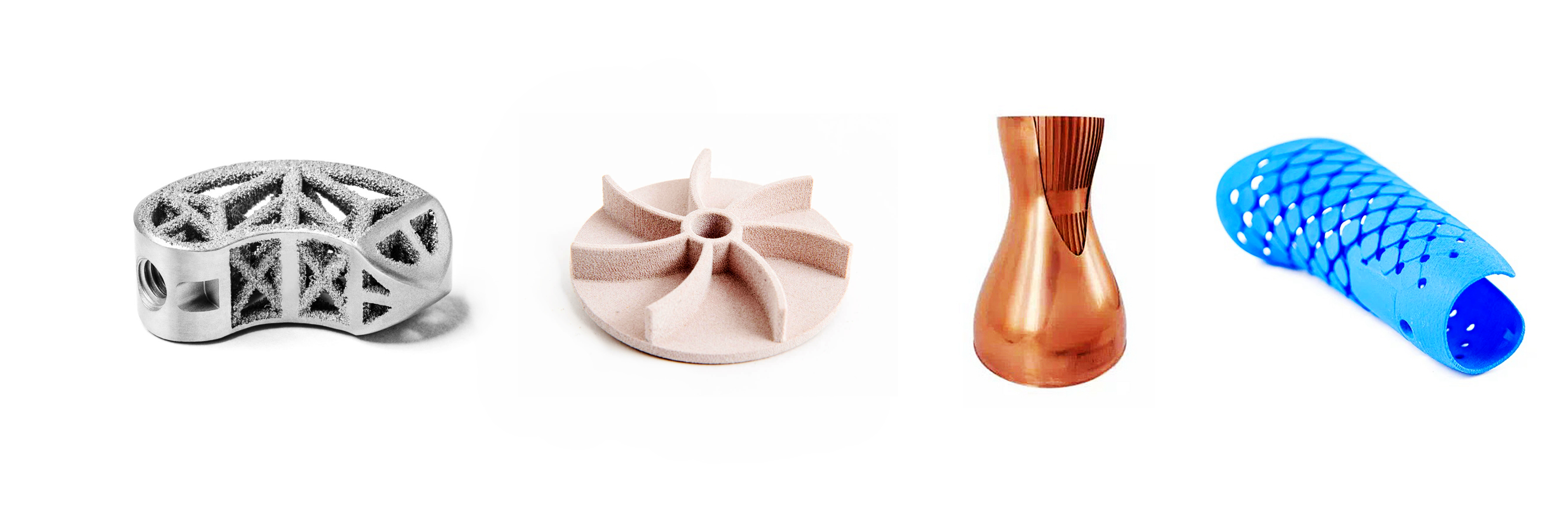
Plastic 3D Printed Parts Gallery
Explore the versatility of plastic 3D printing through our diverse collection of precision-engineered parts. From sleek consumer electronics casings to durable protective gear, intricate jewelry, and educational tools, our gallery showcases innovation in design, functionality, and rapid prototyping. Discover how plastic 3D printing transforms industries with efficiency and creativity.
Let's Start A New Project Today
Plastic 3D Printed Parts Design Considerations
When designing parts for 3D printing in plastic, considerations include managing lower melting points, reducing warping, and ensuring print fidelity. Design strategies focus on optimizing wall thickness, support requirements, and part orientation to utilize the flexibility and versatility of plastic materials effectively.
Plastics 3D Printed Parts Manufacturing Considerations
Manufacturing considerations for plastic 3D printed parts are vital to optimize the production process and enhance the quality and functionality of the final products. This involves selecting suitable materials, controlling the printing environment, and implementing effective post-processing techniques.